| 第一臺服務器 | 192.168.1.1 |
| 第二臺服務器 | 192.168.1.2 |
| 第三臺服務器 | 192.168.1.3 |
第一個請求過來之后默認訪問第一臺,第二個請求過來訪問第二臺,第三次請求過來訪問第三臺,第四次請求過來訪問第一臺,以此類推。以下是我代碼實現(xiàn)簡單得算法:
public class SimplePolling {
/**
* key是ip
*/
public static List <String> ipService = new LinkedList <>();
static {
ipService.add("192.168.1.1");
ipService.add("192.168.1.2");
ipService.add("192.168.1.3");
}
public static int pos = 0;
public static String getIp(){
if(pos >= ipService.size()){
//防止索引越界
pos = 0;
}
String ip = ipService.get(pos);
pos ++;
return ip;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
System.out.println(getIp());
}
}
}
模擬執(zhí)行4次執(zhí)行結果是

此時如果我有一臺服務器性能比較好(比如192.168.1.1),我想讓這臺服務器處理多一點請求,此時就涉及到了權重得概率,這種算法就不能實現(xiàn),請看我后面描述的輪詢升級版算法。
加權輪詢算法
此時我需要把我前面3臺服務器都設置權重,比如第一臺設置5,第二臺設置1,第三臺設置1
| 第一臺服務器 | 192.168.1.1 | 5 |
| 第二臺服務器 | 192.168.1.2 | 1 |
| 第三臺服務器 | 192.168.1.3 | 1 |
此時前5個請求都會訪問到第一臺服務器,第六個請求會訪問到第二臺服務器,第七個請求會訪問到第三臺服務器。
以下是我給出的代碼案例:
public class WeightPolling {
/**
* key是ip,value是權重
*/
public static Map<String, Integer> ipService = new LinkedHashMap<>();
static {
ipService.put("192.168.1.1", 5);
ipService.put("192.168.1.2", 1);
ipService.put("192.168.1.3", 1);
}
public static int requestId = 0;
public static int getAndIncrement() {
return requestId++;
}
public static String getIp(){
//獲取總的權重
int totalWeight =0;
for (Integer value : ipService.values()) {
totalWeight+= value;
}
//獲取當前輪詢的值
int andIncrement = getAndIncrement();
int pos = andIncrement% totalWeight;
for (String ip : ipService.keySet()) {
if(pos < ipService.get(ip)){
return ip;
}
pos -= ipService.get(ip);
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
System.out.println(getIp());
}
}
}
此時運行結果是
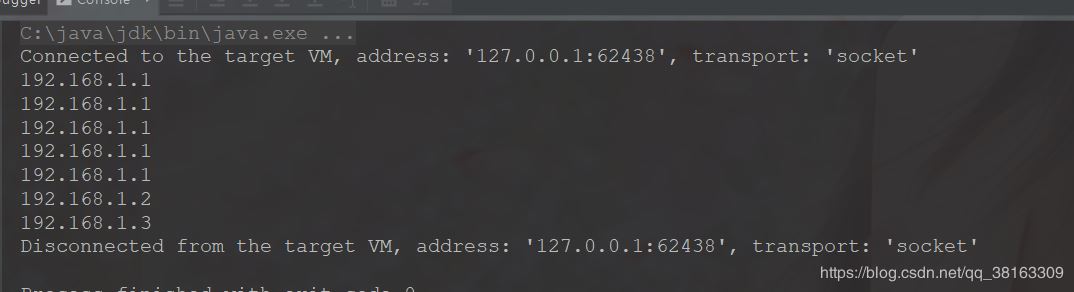
可以看的第一臺服務器執(zhí)行了5次,后面2臺依次執(zhí)行一次,依次類推。可能你覺得這種算法還不錯。其實這種算法有一個缺點是,如果我第一臺服務器設置權重過大可能我需要很多次請求都執(zhí)行到第一臺服務器上去,這樣的情況分布是不均勻的,會造成某一臺服務器壓力過大導致崩潰。所以我后面要引入第三種算法來解決這個問題
平滑加權輪詢算法
這種算法可能比較復雜,我第一次看也有點不太明白,后面看過相關資料在結合我自己的理解給大家圖文解釋一下,這里我舉例的服務器配置和權重還是和上面一樣
| 請求 | 當前權重 = 自身權重+選中后當前權重 | 總權重 | 當前最大權重 | 返回的ip | 選中后當前權重=當前最大權重-總權重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | {5,1,1} | 7 | 5 | 192.168.1.1 | {-2,1,1} |
| 2 | {3,2,2} | 7 | 3 | 192.168.1.1 | {-4,2,2} |
| 3 | {1,3,3} | 7 | 3 | 192.168.1.2 | {1,-4,3} |
| 4 | {6,-3,4} | 7 | 6 | 192.168.1.1 | {-1,-3,4} |
| 5 | {4,-2,5} | 7 | 5 | 192.168.1.3 | {4,-2,-2} |
| 6 | {9,-1,-1} | 7 | 9 | 192.168.1.1 | {2,-1,-1} |
| 7 | {7,0,0} | 7 | 7 | 192.168.1.1 | {0,0,0} |
由上圖可以看出第一臺服務器雖然權重設置的是5,但并不是第五次請求過來都是第一臺服務器執(zhí)行,而是分散執(zhí)行,調(diào)度序列是非常均勻的,且第 7 次調(diào)度時選中后當前權重又回到 {0, 0, 0},實例的狀態(tài)同初始狀態(tài)一致,所以后續(xù)可以一直重復調(diào)度操作。
可能有的人還不能清楚的明白上一張圖表示的含義,我這里大概描述一下:
1.首先總權重不會變,默認就是當前設置的權重之和
2.在第一次請求進來的時候我默認初始化當前權重選中值是{0,0,0},所以當前權重的值就是{5+0,1+0,1+0},這里的5,1,1就是我們前面每臺服務器設置的權重。
3.這里我們可以得出第一次請求過來的最大權重是5。然后返回第一臺服務器ip
4.然后我們設置選中后當前權重,這里就是當前最大權重減去總權重(5-7),沒有選中的權重不變,這時候得到當前權重選中權重的值{5-7,1,1}
5.在第二次請求過來的時候我們延續(xù)上面的2,3,4步驟執(zhí)行.
如果這里還有不懂得我下面會提供我自己用java代碼實現(xiàn)的算法:
public class Polling {
/**
* key是ip,value是權重
*/
public static Map <String,Integer> ipService = new LinkedHashMap <>();
static {
ipService.put("192.168.1.1",5);
ipService.put("192.168.1.2",1);
ipService.put("192.168.1.3",1);
}
private static Map<String,Weight> weightMap = new LinkedHashMap <>();
public static String getIp(){
//計算總的權重
int totalWeight = 0;
for (Integer value : ipService.values()) {
totalWeight+=value;
}
//首先判斷weightMap是否為空
if(weightMap.isEmpty()){
ipService.forEach((ip,weight)->{
Weight weights = new Weight(ip, weight,0);
weightMap.put(ip,weights);
});
}
//給map中得對象設置當前權重
weightMap.forEach((ip,weight)->{
weight.setCurrentWeight(weight.getWeight() + weight.getCurrentWeight());
});
//判斷最大權重是否大于當前權重,如果為空或者小于當前權重,則把當前權重賦值給最大權重
Weight maxWeight = null;
for (Weight weight : weightMap.values()) {
if(maxWeight ==null || weight.getCurrentWeight() > maxWeight.getCurrentWeight()){
maxWeight = weight;
}
}
//最后把當前最大權重減去總的權重
maxWeight.setCurrentWeight(maxWeight.getCurrentWeight() - totalWeight);
//返回
return maxWeight.getIp();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模擬輪詢7次取ip
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
System.out.println(getIp());
}
}
}
class Weight{
/**
* ip
*/
private String ip;
/**
* 設置得權重
*/
private int weight;
/**
* 當前權重
*/
private int currentWeight;
public Weight(String ip, int weight,int currentWeight) {
this.ip = ip;
this.weight = weight;
this.currentWeight = currentWeight;
}
public String getIp() {
return ip;
}
public void setIp(String ip) {
this.ip = ip;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getCurrentWeight() {
return currentWeight;
}
public void setCurrentWeight(int currentWeight) {
this.currentWeight = currentWeight;
}
}
這里代碼得執(zhí)行結果是:

可以看出此處執(zhí)行結果和表格里描述得結果一致。
總結
可能第三種算法理解起來有點復雜,如果看不懂圖表得意思可以先執(zhí)行下代碼,debugger一步步調(diào)試后還是很好理解。
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持腳本之家。